Climate variability
Sometimes the terms “climate change” and “climate variability” are used interchangeably, but they are not quite the same. Climate variability refers to natural variation in climate that occurs over months to decades.
Climate variability means short-term changes in climate that occur within smaller time frames, such as a month, a season or a year.
Scientists believe that the climate variations are caused by many natural factors, including
- changes in the sun (its brightness, levels of solar radiation, solar flares and sunspot activity)
- emissions from volcanoes
- variations in the Earth’s orbit
- levels of carbon dioxide (CO2)
Climatologists have identified natural climate variability cycles that tend to occur in intervals in different regions. A good example of natural climate variability is the El Niño and La Niña climatic occurrences, which change temperature, rain and wind patterns in many regions over a period of about two to seven years. El Niño and La Niña are the two phases of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (sometimes shortened to ENSO). El Niño usually brings wetter and warmer than normal conditions and can cause floods, while La Niña brings cooler, drier conditions or drought.
Climate Variability and Climate Change
This video explains the difference between climate change and climate variability.
ARVE error: maxwidth: 560px is not valid
If you have trouble accessing the video, a summary is available below.
Study the graph Mean-Temperature Annual Trends showing climatic variability in terms of mean (average) temperatures for Botswana. Answer the questions that follow.
1. Describe the mean annual temperatures of the period between 1950 and 1960 and also for the period between 1968 and 1975. Is this trend an example of climate variability or climate change?
2. Study the mean annual temperature trends as shown in the key to the graph. Describe the general trend of all three periods. Would you say that from 1950 to 2020, the mean annual temperature has been increasing or decreasing? Is this an example of climate variability or climate change?
3. Climate variability and climate change are not quite the same. Study the figure below; it illustrates the difference in timescales.
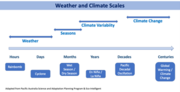
Weather and Climate Change Scales. Adapted from Pacific Australia Science and Adaptation Planning Program & Eco-Intelligent
Now that you understand that climate variability is mostly a natural occurrence within the climate system or from other non-human external forces, it is also important to understand, at this point, that climate change is causing an increase in the probability of many extreme weather events, and those events contribute to climate variability.
References
- ↑ The World Bank, 2023.Climate Trends
Climate variability
Sometimes the terms “climate change” and “climate variability” are used interchangeably, but they are not quite the same. Climate variability refers to natural variation in climate that occurs over months to decades.
Climate variability means short-term changes in climate that occur within smaller time frames, such as a month, a season or a year.
Scientists believe that the climate variations are caused by many natural factors, including
Climatologists have identified natural climate variability cycles that tend to occur in intervals in different regions. A good example of natural climate variability is the El Niño and La Niña climatic occurrences, which change temperature, rain and wind patterns in many regions over a period of about two to seven years. El Niño and La Niña are the two phases of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (sometimes shortened to ENSO). El Niño usually brings wetter and warmer than normal conditions and can cause floods, while La Niña brings cooler, drier conditions or drought.
Climate Variability and Climate Change
This video explains the difference between climate change and climate variability.
ARVE error: maxwidth:
560pxis not validIf you have trouble accessing the video, a summary is available below.
Activity
Study the graph Mean-Temperature Annual Trends showing climatic variability in terms of mean (average) temperatures for Botswana. Answer the questions that follow.
1. Describe the mean annual temperatures of the period between 1950 and 1960 and also for the period between 1968 and 1975. Is this trend an example of climate variability or climate change?
2. Study the mean annual temperature trends as shown in the key to the graph. Describe the general trend of all three periods. Would you say that from 1950 to 2020, the mean annual temperature has been increasing or decreasing? Is this an example of climate variability or climate change?
3. Climate variability and climate change are not quite the same. Study the figure below; it illustrates the difference in timescales.
Now that you understand that climate variability is mostly a natural occurrence within the climate system or from other non-human external forces, it is also important to understand, at this point, that climate change is causing an increase in the probability of many extreme weather events, and those events contribute to climate variability.
References
Project lead
Supported by
Development Partner